Abstract
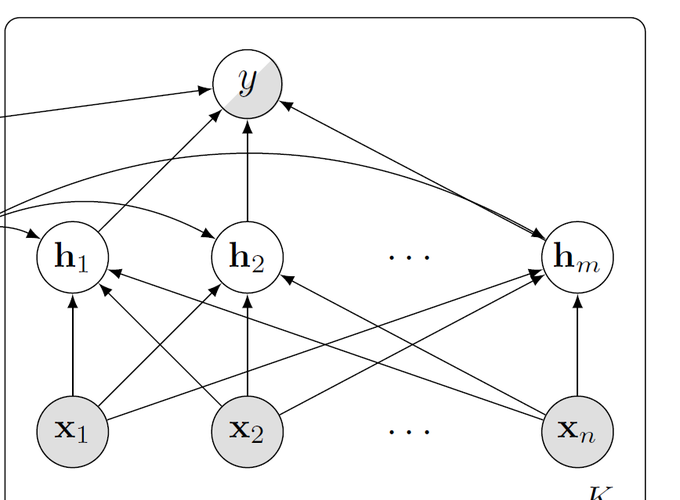
While achieving state-of-the-art results in multiple tasks and languages, translation-based cross-lingual transfer is often overlooked in favour of massively multilingual pre-trained encoders. Arguably, this is due to its main limitations: 1) translation errors percolating to the classification phase and 2) the insufficient expressiveness of the maximum-likelihood translation. To remedy this, we propose a new technique that integrates both steps of the traditional pipeline (translation and classification) into a single model, by treating the intermediate translations as a latent random variable. As a result, 1) the neural machine translation system can be fine-tuned with a variant of Minimum Risk Training where the reward is the accuracy of the downstream task classifier. Moreover, 2) multiple samples can be drawn to approximate the expected loss across all possible translations during inference. We evaluate our novel latent translation-based model on a series of multilingual NLU tasks, including commonsense reasoning, paraphrase identification, and natural language inference. We report gains for both zero-shot and few-shot learning setups, up to 2.7 accuracy points on average, which are even more prominent for low-resource languages (e.g., Haitian Creole). Finally, we carry out in-depth analyses comparing different underlying NMT models and assessing the impact of alternative translations on the downstream performance.